PCIE-LINUX DMA驱动编写与测试
2024-09-14
252
0
一、前言
代码参考:https://gitee.com/daalw/PCIe_Driver_Demo
通过查看docs/specs/edu.txt可以知道 EDU 设备是支持DMA的
EDU device==========Copyright (c) 2014-2015 Jiri SlabyThis document is licensed under the GPLv2 (or later).This is an educational device for writing (kernel) drivers. Its originalintention was to support the Linux kernel lectures taught at the MasarykUniversity. Students are given this virtual device and are expected to write adriver with I/Os, IRQs, DMAs and such.The devices behaves very similar to the PCI bridge present in the COMBO6 cardsdeveloped under the Liberouter wings. Both PCI device ID and PCI space isinherited from that device.Command line switches:-device edu[,dma_mask=mask]dma_mask makes the virtual device work with DMA addresses with the givenmask. For educational purposes, the device supports only 28 bits (256 MiB)by default. Students shall set dma_mask for the device in the OS driverproperly.PCI specs---------PCI ID: 1234:11e8PCI Region 0:I/O memory, 1 MB in size. Users are supposed to communicate with the cardthrough this memory.MMIO area spec--------------Only size == 4 accesses are allowed for addresses < 0x80. size == 4 orsize == 8 for the rest.0x00 (RO) : identification (0xRRrr00edu)RR -- major versionrr -- minor version0x04 (RW) : card liveness checkIt is a simple value inversion (~ C operator).0x08 (RW) : factorial computationThe stored value is taken and factorial of it is put back here.This happens only after factorial bit in the status register (0x20below) is cleared.0x20 (RW) : status register, bitwise OR0x01 -- computing factorial (RO)0x80 -- raise interrupt 0x01 after finishing factorial computation0x24 (RO) : interrupt status registerIt contains values which raised the interrupt (see interrupt raiseregister below).0x60 (WO) : interrupt raise registerRaise an interrupt. The value will be put to the interrupt statusregister (using bitwise OR).0x64 (WO) : interrupt acknowledge registerClear an interrupt. The value will be cleared from the interruptstatus register. This needs to be done from the ISR to stopgenerating interrupts.0x80 (RW) : DMA source addressWhere to perform the DMA from.0x88 (RW) : DMA destination addressWhere to perform the DMA to.0x90 (RW) : DMA transfer countThe size of the area to perform the DMA on.0x98 (RW) : DMA command register, bitwise OR0x01 -- start transfer0x02 -- direction (0: from RAM to EDU, 1: from EDU to RAM)0x04 -- raise interrupt 0x100 after finishing the DMAIRQ controller--------------An IRQ is generated when written to the interrupt raise register. The valueappears in interrupt status register when the interrupt is raised and has tobe written to the interrupt acknowledge register to lower it.DMA controller--------------One has to specify, source, destination, size, and start the transfer. One4096 bytes long buffer at offset 0x40000 is available in the EDU device. I.e.one can perform DMA to/from this space when programmed properly.Example of transferring a 100 byte block to and from the buffer using a givenPCI address 'addr':addr -> DMA source address0x40000 -> DMA destination address100 -> DMA transfer count1 -> DMA command registerwhile (DMA command register & 1);0x40000 -> DMA source addressaddr+100 -> DMA destination address100 -> DMA transfer count3 -> DMA command registerwhile (DMA command register & 1);
三、驱动编写
编写驱动代码如下所示:
#include <linux/kernel.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/pci.h>#include <linux/init.h>#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/errno.h>#include <linux/cdev.h>#include <linux/device.h>#include <linux/dma-mapping.h>#define HELLO_PCI_DEVICE_ID 0x11e8#define HELLO_PCI_VENDOR_ID 0x1234#define HELLO_PCI_REVISION_ID 0x10#define ONCHIP_MEM_BASE 0x40000static struct pci_device_id ids[] = {{ PCI_DEVICE(HELLO_PCI_VENDOR_ID, HELLO_PCI_DEVICE_ID), },{ 0 , }};static struct hello_pci_info_t {dev_t dev_id;struct cdev char_dev;struct class *class;struct device *device;struct pci_dev *pdev;void __iomem *address_bar0;atomic_t dma_running;spinlock_t lock;wait_queue_head_t r_wait;} hello_pci_info;MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(pci, ids);static irqreturn_t hello_pci_irq_handler(int irq, void *dev_info){struct hello_pci_info_t *_pci_info = dev_info;uint32_t irq_status;// get irq_stutasirq_status = *((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x24));printk("hello_pcie: get irq status: 0x%0x\n", irq_status);// clean irq*((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x64)) = irq_status;// get irq_stutasirq_status = *((uint32_t *)(_pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x24));if(irq_status == 0x00){printk("hello_pcie: receive irq and clean success. \n");}else{printk("hello_pcie: receive irq but clean failed !!! \n");return IRQ_NONE;}atomic_set(&(_pci_info->dma_running), 0);wake_up_interruptible(&(_pci_info->r_wait));return IRQ_HANDLED;}/** @description : 打开设备* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode* @param - file : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败*/static int hello_pcie_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){printk("hello_pcie: open dev file.\n");init_waitqueue_head(&hello_pci_info.r_wait);return 0;}/** @description : 关闭/释放设备* @param - file : 要关闭的设备文件(文件描述符)* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败*/static int hello_pcie_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file){printk("hello_pcie: close dev file.\n");return 0;}//dma transefer from RC to EPint dma_write_block(dma_addr_t dma_handle_addr, int count, struct hello_pci_info_t *_pci_info){spin_lock(&_pci_info->lock);//源地址低32位iowrite32((uint32_t)(dma_handle_addr), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x80);//源地址高32位iowrite32((uint32_t)(dma_handle_addr>>32), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x84);//目的地址低32位iowrite32(ONCHIP_MEM_BASE, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x88);//目的地址高32位iowrite32(0x0, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x8c);//传输长度iowrite32(count, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x90);//启动DMA一次iowrite32((0x01) | (0x00<<1) | (0x01<<2), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x98);spin_unlock(&_pci_info->lock);return 0;}//dma transefer from EP to RCint dma_read_block(dma_addr_t dma_handle_addr, int count, struct hello_pci_info_t *_pci_info){spin_lock(&_pci_info->lock);// 源地址低32位iowrite32(ONCHIP_MEM_BASE, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x80);// 源地址高32位iowrite32(0, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x84);// 目的地址低32位iowrite32((uint32_t)(dma_handle_addr), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x88);// 目的地址高32位iowrite32((uint32_t)(dma_handle_addr>>32), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x8c);// 传输长度iowrite32(count, _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x90);// 启动DMA一次iowrite32((0x01) | (0x01<<1) | (0x01<<2), _pci_info->address_bar0 + 0x98);spin_unlock(&_pci_info->lock);return 0;}/** @description : 向设备写数据* @param - pfile : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败*/static ssize_t hello_pcie_write(struct file *pfile, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt){int ret;unsigned char * databuf;dma_addr_t dma_handle_addr;if(cnt > 4096){printk("hello_pcie: dma does not support transfers larger than 4096.\n");return -ENOMEM;}databuf = dma_alloc_coherent(&hello_pci_info.pdev->dev, 4096, &dma_handle_addr, GFP_KERNEL);if (!databuf) {printk("hello_pcie: Failed to allocate DMA buffer\n");return -ENOMEM;}else {printk("hello_pcie: get dma_handle_addr success: 0x%0llx\n", dma_handle_addr);}ret = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);if(ret < 0) {printk("hello_pcie: write failed!\n");return -EFAULT;}dma_write_block(dma_handle_addr, cnt, &hello_pci_info);atomic_set(&hello_pci_info.dma_running, 1);ret = wait_event_interruptible(hello_pci_info.r_wait, 0 == atomic_read(&hello_pci_info.dma_running));dma_free_coherent(&hello_pci_info.pdev->dev, 4096, databuf, dma_handle_addr);return ret;}/** @description : 从设备读取数据* @param – filp : 要打开的设备文件(文件描述符)* @param – buf : 返回给用户空间的数据缓冲区* @param – cnt : 要读取的数据长度* @param – offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移* @return : 读取的字节数,如果为负值,表示读取失败*/static ssize_t hello_pcie_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt){int ret;unsigned char * databuf;dma_addr_t dma_handle_addr;if(cnt > 4096){printk("hello_pcie: dma does not support transfers larger than 4096.\n");return -ENOMEM;}databuf = dma_alloc_coherent(&hello_pci_info.pdev->dev, 4096, &dma_handle_addr, GFP_KERNEL);if (!databuf) {printk("hello_pcie: Failed to allocate DMA buffer\n");return -ENOMEM;}else {printk("hello_pcie: get dma_handle_addr success: 0x%0llx\n", dma_handle_addr);}dma_read_block(dma_handle_addr, cnt, &hello_pci_info);atomic_set(&hello_pci_info.dma_running, 1);/* 加入等待队列,当有DMA传输完成时,才会被唤醒 */ret = wait_event_interruptible(hello_pci_info.r_wait, 0 == atomic_read(&hello_pci_info.dma_running));if(ret)return ret;memset(buf, 0, cnt);ret = copy_to_user(buf, databuf, cnt);dma_free_coherent(&hello_pci_info.pdev->dev, 4096, databuf, dma_handle_addr);return ret;}/* device file operations function */static struct file_operations hello_pcie_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = hello_pcie_open,.release = hello_pcie_close,.read = hello_pcie_read,.write = hello_pcie_write,};static int hello_pcie_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *id){int bar = 0;int ret;resource_size_t len;ret = pci_enable_device(pdev);if(ret) {return ret;}pci_set_master(pdev);if (!pci_set_dma_mask(pdev, DMA_BIT_MASK(28))){pci_set_consistent_dma_mask(pdev, DMA_BIT_MASK(28));dev_info(&pdev->dev, "using a 28-bit dma mask\n");}else{dev_info(&pdev->dev, "unable to use 28-bit dma mask\n");return -1;}len = pci_resource_len(pdev, bar);hello_pci_info.address_bar0 = pci_iomap(pdev, bar, len);hello_pci_info.pdev = pdev;// register interruptret = request_irq(pdev->irq, hello_pci_irq_handler, IRQF_SHARED, "hello_pci", &hello_pci_info);if(ret) {printk("request IRQ failed.\n");return ret;}// enable irq for finishing factorial computation*((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x20)) = 0x80;return 0;}static void hello_pcie_remove(struct pci_dev *pdev){// disable irq for finishing factorial computation*((uint32_t *)(hello_pci_info.address_bar0 + 0x20)) = 0x01;free_irq(pdev->irq, &hello_pci_info);pci_iounmap(pdev, hello_pci_info.address_bar0);pci_disable_device(pdev);}static struct pci_driver hello_pci_driver = {.name = "hello_pcie",.id_table = ids,.probe = hello_pcie_probe,.remove = hello_pcie_remove,};static int __init hello_pci_init(void){int ret = pci_register_driver(&hello_pci_driver);if(hello_pci_info.pdev == NULL){printk("hello_pci: probe pcie device failed!\n");return ret;}/* 1、Request device number */ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&hello_pci_info.dev_id, 0, 1, "hello_pcie");/* 2、Initial char_dev */hello_pci_info.char_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;cdev_init(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, &hello_pcie_fops);/* 3、add char_dev */cdev_add(&hello_pci_info.char_dev, hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1);/* 4、create class */hello_pci_info.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_pcie");if (IS_ERR(hello_pci_info.class)) {return PTR_ERR(hello_pci_info.class);}/* 5、create device */hello_pci_info.device = device_create(hello_pci_info.class, NULL, hello_pci_info.dev_id, NULL, "hello_pcie");if (IS_ERR(hello_pci_info.device)) {return PTR_ERR(hello_pci_info.device);}return ret;}static void __exit hello_pci_exit(void){if(hello_pci_info.pdev != NULL) {cdev_del(&hello_pci_info.char_dev); /* del cdev */unregister_chrdev_region(hello_pci_info.dev_id, 1); /* unregister device number */device_destroy(hello_pci_info.class, hello_pci_info.dev_id);class_destroy(hello_pci_info.class);}pci_unregister_driver(&hello_pci_driver);}module_init(hello_pci_init);module_exit(hello_pci_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");MODULE_INFO(intree, "Y");
注意其中的 pci_set_dma_mask和pci_set_consistent_dma_mask就是为了适应28bit的DMA地址做的适配。
四、编写用户程序
编写用户测试程序testapp.c如下:
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdint.h"#include "unistd.h"#include "sys/types.h"#include "sys/stat.h"#include "fcntl.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "string.h"#define BUFFER_LENGTH 128int main(int argc, char *argv[]){int fd, retvalue;char *filename = "/dev/hello_pcie";unsigned char *write_buf = malloc(BUFFER_LENGTH);unsigned char *read_buf = malloc(BUFFER_LENGTH);/* 打开驱动设备文件 */fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){printf("file %s open failed!\n", filename);return -1;}for(int i = 0;i < BUFFER_LENGTH;i++){write_buf[i] = i;}/* 向/dev/hello_pcie文件写入数据 */retvalue = write(fd, write_buf, BUFFER_LENGTH);if(retvalue < 0){printf("Write %s Failed!\n", filename);close(fd);return -1;}printf("write success, data: 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x\n", write_buf[0], write_buf[1], write_buf[2], write_buf[3], write_buf[4], write_buf[5], write_buf[6], write_buf[7]);retvalue = read(fd, read_buf, BUFFER_LENGTH);if(retvalue < 0){printf("Read %s Failed!\n", filename);close(fd);return -1;}printf("read success, data: 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x, 0x%0x\n", read_buf[0], read_buf[1], read_buf[2], read_buf[3], read_buf[4], read_buf[5], read_buf[6], read_buf[7]);retvalue = close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */if(retvalue < 0){printf("file %s close failed!\r\n", filename);return -1;}return 0;}
五、运行测试
编译加载驱动,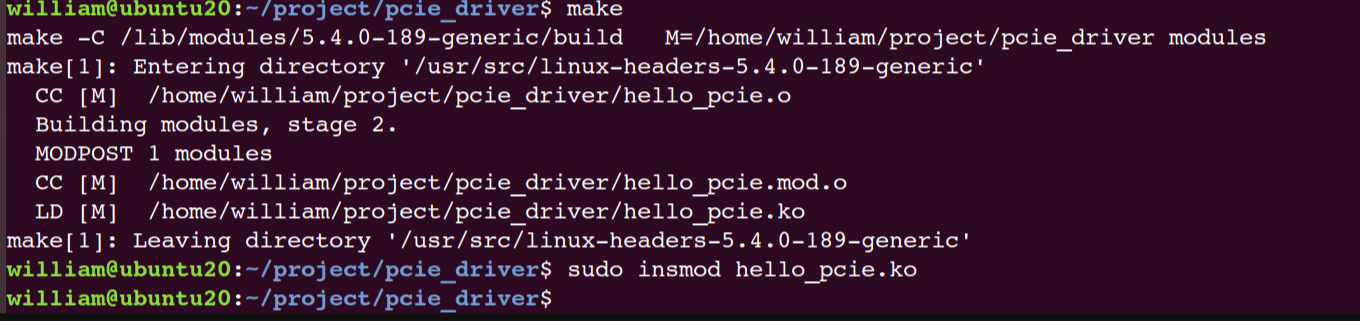
使用如下命令编译测试程序:
gcc testapp.c
然后运行测试程序,可以看到符合预期结果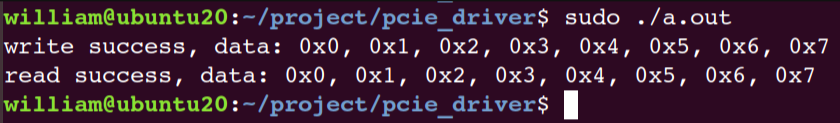
 一个最简单的LINUX-PCIE设备驱动
一个最简单的LINUX-PCIE设备驱动





